Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
神谷 富裕; 佐藤 隆博; 江夏 昌志; 加田 渉*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 348, p.4 - 7, 2015/04
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:39.96(Instruments & Instrumentation)Ion microbeam technology has been progressed at TIARA, aiming at expanding its applications. Micro-analyses of micro-PIGE and micro-IBIL (Ion Beam Induced Luminescence) based on the micro-PIXE have expanded a region of their analyzing objects. Micro-fabrication by mask-less irradiation on materials based on the technique of PBW (Proton Beam Writing) without etching processes was applied for optical, magnetic or other novel micro-devices fabrication. Single-ion-hitting technique which was required for reliable irradiation to biological cells or semiconductor devices progressed so that each ion hit could be monitored in real time using an efficient scintillator and a high sensitivity camera. Development of a thin film type particle detector was newly started for the same purpose. This paper summarizes the latest progress of the ion microbeam technology and applications at TIARA, and discusses their future prospects.
石井 保行; 大久保 猛; 神谷 富裕; 齋藤 勇一
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 348, p.79 - 82, 2015/04
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:17.57(Instruments & Instrumentation)A hundreds-keV compact ion microbeam system with a three-stage acceleration lens is under development to form an ion beam of several micrometers in diameter. A proton beam of 17 m in diameter was formed in the previous study and the smaller beam size could be expected at the lower pressure. In this study, the vacuum system at the extraction space was improved and the relation between the beam size and vacuum pressure was examined by forming hydrogen ion beams at 130 keV. As a result, the beam size of 5.8
m in diameter was formed in the previous study and the smaller beam size could be expected at the lower pressure. In this study, the vacuum system at the extraction space was improved and the relation between the beam size and vacuum pressure was examined by forming hydrogen ion beams at 130 keV. As a result, the beam size of 5.8  m which almost satisfied our present goal was obtained at the achievably lowest pressure (5
m which almost satisfied our present goal was obtained at the achievably lowest pressure (5 10
10 Pa).
Pa).
加田 渉*; 神林 佑哉*; 岩本 直也*; 小野田 忍; 牧野 高紘; 江夏 昌志; 神谷 富裕; 星乃 紀博*; 土田 秀一*; 児島 一聡*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 348, p.240 - 245, 2015/04
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:33.25(Instruments & Instrumentation)Deep level defects in semiconductors act as carrier traps Deep Level Transient Spectroscopy (DLTS) is known as one of the most famous techniques to investigate deep levels. However, DLTS does not well work for samples with high resistivity. To overcome this issue, DLTS using charge generated by ion incidence was proposed. Recently, we developed a deep level evaluation system based on Charge Transient Spectroscopy using alpha particles from  Am (Alpha Particle Charge Transient Spectroscopy: APQTS) and reported the effect of deep levels in 6H SiC pn diodes generated by electron irradiation on the characteristics as particle detectors. In this study, we report the development of Charge Transient Spectroscopy using Heavy Ion Microbeams (HIQTS). The HIQTS can detect deep levels with micron meter spatial resolution since microbeams are applied. Thus, we can clarify the relationship between deep levels and device characteristics with micron meter resolution. When a 6H-SiC pn diode was irradiated with 12 MeV-oxygen (O) ions at 4
Am (Alpha Particle Charge Transient Spectroscopy: APQTS) and reported the effect of deep levels in 6H SiC pn diodes generated by electron irradiation on the characteristics as particle detectors. In this study, we report the development of Charge Transient Spectroscopy using Heavy Ion Microbeams (HIQTS). The HIQTS can detect deep levels with micron meter spatial resolution since microbeams are applied. Thus, we can clarify the relationship between deep levels and device characteristics with micron meter resolution. When a 6H-SiC pn diode was irradiated with 12 MeV-oxygen (O) ions at 4 10
10 and 8
and 8 10
10 /cm
/cm , the charge collection efficiency (CCE) decreased to 71 and 52%, respectively. HIQTS signals obtained from those damaged regions using 15 MeV-O microbeams increased at measurement temperature ranges above 350 K, and the signals are larger with increasing 12 MeV-O ion fluence.
, the charge collection efficiency (CCE) decreased to 71 and 52%, respectively. HIQTS signals obtained from those damaged regions using 15 MeV-O microbeams increased at measurement temperature ranges above 350 K, and the signals are larger with increasing 12 MeV-O ion fluence.
加田 渉*; 三浦 健太*; 加藤 聖*; 猿谷 良太*; 久保田 篤志*; 佐藤 隆博; 江夏 昌志; 石井 保行; 神谷 富裕; 西川 宏之*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 348, p.218 - 222, 2015/04
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:45.92(Instruments & Instrumentation)The Mach-Zehnder (MZ) optical structures were previously fabricated in a Poly-methyl-methacrylate (PMMA) thin film by Proton Beam Writing (PBW). The enhancement of optical transmittance in the structures is, however, required for industrial use. In this study, the MZ optical waveguides have been fabricated in a poly-dimethyl-siloxane (PDMS) thin film which has the higher optical permeability. The PDMS films were spin-coated on a silicon wafer (40  20
20  0.5 mm
0.5 mm ) with a thickness of approximately 30
) with a thickness of approximately 30  m. The MZ waveguides were drawn by a 750 keV proton microbeam of 1
m. The MZ waveguides were drawn by a 750 keV proton microbeam of 1 m in diameter having the penetration depth of 18
m in diameter having the penetration depth of 18  m with fluence of 40-100 nC/mm
m with fluence of 40-100 nC/mm . The beam writing was carried out combining an electric scanner and a mechanical sample-stage. The observation of the single-mode light propagation of 1.55
. The beam writing was carried out combining an electric scanner and a mechanical sample-stage. The observation of the single-mode light propagation of 1.55  m fiber-laser in the MZ waveguides indicated that the optical transmittance have been successfully enhanced using PDMS.
m fiber-laser in the MZ waveguides indicated that the optical transmittance have been successfully enhanced using PDMS.
Pastuovi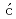 ,
, 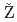 *; Capan, I.*; Cohen, D.*; Forneris, J.*; 岩本 直也*; 大島 武; Siegele, R.*; 星乃 紀博*; 土田 秀一*
*; Capan, I.*; Cohen, D.*; Forneris, J.*; 岩本 直也*; 大島 武; Siegele, R.*; 星乃 紀博*; 土田 秀一*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 348, p.233 - 239, 2015/04
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:51.25(Instruments & Instrumentation)The relationship between defects created in SiC semiconductors and the degradation of SiC particle detectors was investigated. The n-type Schottky barrier diodes (SBD) fabricated on an epitaxial 4H-SiC layer were irradiated with a raster scanned alpha particle microbeam (either 2 or 4 MeV He ions) to introduce crystal damage with different depths. Deep level transient spectroscopy (DLTS) was applied to characterize defects generated in SiC by He ion irradiation. Ion Beam Induced Charge (IBIC) microscopy was used to determine the degradation of the charge collection efficiency (CCE). DLTS and electrical characteristics measurements suggested that minority carrier lifetime decreased with increasing the concentration of Z
ions) to introduce crystal damage with different depths. Deep level transient spectroscopy (DLTS) was applied to characterize defects generated in SiC by He ion irradiation. Ion Beam Induced Charge (IBIC) microscopy was used to determine the degradation of the charge collection efficiency (CCE). DLTS and electrical characteristics measurements suggested that minority carrier lifetime decreased with increasing the concentration of Z defect. Also, the free carrier concentration in SiC decreased with increasing He fluence. Furthermore, the formation of new type of defects, i.e. complex (cluster) defects was detected. In conclusion, the value of CCE decreased due to above-mentioned effects.
defect. Also, the free carrier concentration in SiC decreased with increasing He fluence. Furthermore, the formation of new type of defects, i.e. complex (cluster) defects was detected. In conclusion, the value of CCE decreased due to above-mentioned effects.
山崎 明義*; 神谷 富裕; 佐藤 隆博; 三間 圀興*; 藤田 和久*; 奥田 匠昭*; 佐和田 博*; 斎藤 俊哉*; Gonzales, R.*; Perlado, J. M.*; et al.
no journal, ,
For the development of advanced lithium (Li) ion batteries, precise diagnostics of Li in the electrode material is required. In order to obtain specific distribution of Li in Li ion battery materials, we have utilised the nuclear reaction analysis (NRA) and the particle induced  -ray emission analysis (PIGE) with the micro-PIXE analysis, which characterises the heavier elements, in the proton microbeam system at TIARA. The Li distribution in real Li-ion batteries was analysed mainly in the cross-sections of fabricated electrode samples containing micro particles based on metal oxides. The objects of the analyses were extended to all-solid batteries as the candidate for the next generation Li ion battery. The obtained images show the distributions of the Li ions buried in the electrode materials varying with charging condition and other various factors. This paper describes the analysis system and results of the experiments.
-ray emission analysis (PIGE) with the micro-PIXE analysis, which characterises the heavier elements, in the proton microbeam system at TIARA. The Li distribution in real Li-ion batteries was analysed mainly in the cross-sections of fabricated electrode samples containing micro particles based on metal oxides. The objects of the analyses were extended to all-solid batteries as the candidate for the next generation Li ion battery. The obtained images show the distributions of the Li ions buried in the electrode materials varying with charging condition and other various factors. This paper describes the analysis system and results of the experiments.
長嶺 竹明*; 富岡 智*; 佐藤 隆博; 江夏 昌志; 神谷 富裕
no journal, ,
Chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients treated with pegulated-interferon, ribavirin (Peg-IFN+RBV) and teraprevir (Peg-IFN+RBV+TPV) are frequently associated with anemia. This study is aimed at analyzing the elemental changes in erythrocytes to investigate the pathogenesis of anemia caused by combination of Peg-IFN and anti-viral drugs. Thirteen CHC patients (3 cases without IFN therapy, 7 cases treated with Peg-IFN+RBV, 3 cases treated with Peg-IFN+RBV+TPV) and 4 healthy controls were enrolled in this study. Whole blood was collected via peripheral vein, and prepared for PIXE analysis. Elemental distribution and elemental levels in erythrocytes were analyzed by in-air microPIXE at JAEA-Takasaki. The elemental distributions in erythrocytes were changed in CHC patients by receiving Peg-IFN+RBV. In addition, erythrocytes elements were altered by Peg-IFN+RBV+TPV, suggesting that the pathogenesis of anemia was different between Peg-IFN+RVB therapy and Peg-IFN+RBV+TPV therapy.
西川 宏之*; 鮎瀬 銀也*; 時田 寛也*; 内田 諭*; 佐藤 隆博; 石井 保行; 神谷 富裕
no journal, ,
Dielectrophoresis (DEP) has been widely used to trap micro particles and microbes such as E.coli. We previously reported the introduction of the DEP devices with SU-8 high-aspect-pillar arrays on a silicon substrate by proton beam writing (PBW) so as to improve their trapping capability. In this study, new DEP devices with the SU-8 high-aspect-pillar arrays have been fabricated on a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film to add bendability. The fabrication was performed with proton beams (1.0-1.7 MeV, 1.0  m
m  ). The proton fluence to form the pillar on the PET film was determined in the experiments. As a result, the bendable DEP devices with the pillar arrays were successfully developed on the PET films to be widely used in industries.
). The proton fluence to form the pillar on the PET film was determined in the experiments. As a result, the bendable DEP devices with the pillar arrays were successfully developed on the PET films to be widely used in industries.
加田 渉*; 小野田 忍; 岩本 直也*; 星乃 紀博*; 土田 秀一*; 牧野 高紘; 神林 佑哉; 江夏 昌志; 花泉 修*; 神谷 富裕; et al.
no journal, ,
Charge transient spectroscopy (QTS) techniques using ionizing particle probes, 5.5 MeV alpha particles from an  Am radiation source (APQTS) and focused heavy ions (10.5 MeV oxygen) from a 3 MV tandem accelerator (HIQTS) were applied in order to investigate effects of deep levels on the Charge Collection Efficiency (CCE) of Schottky Barrier Diodes (SBDs) fabricated on 4H Silicon Carbide (SiC). The degradation of CCE for 4H-SiC SBDs irradiated with 3 MeV protons at 10
Am radiation source (APQTS) and focused heavy ions (10.5 MeV oxygen) from a 3 MV tandem accelerator (HIQTS) were applied in order to investigate effects of deep levels on the Charge Collection Efficiency (CCE) of Schottky Barrier Diodes (SBDs) fabricated on 4H Silicon Carbide (SiC). The degradation of CCE for 4H-SiC SBDs irradiated with 3 MeV protons at 10 /cm
/cm was observed. The APQTS and HIQTS measurements for the irradiated 4H-SiC SBDs were performed. As a result, a deep level at an activation energy of 0.73 eV was detected from the irradiated 4H-SiC SBDs.
was observed. The APQTS and HIQTS measurements for the irradiated 4H-SiC SBDs were performed. As a result, a deep level at an activation energy of 0.73 eV was detected from the irradiated 4H-SiC SBDs.
Skukan, N.*; Grilj, V.*; Pomorski, M.*; 加田 渉*; 岩本 直也*; 大島 武; 神谷 富裕; Jaksic, M.*
no journal, ,
In order to develop diamond thin film detectors, an approximately 6  m thick membrane which was made of low cost optical quality scCVD diamond material was fabricated. The membrane was mounted to a flange as a vacuum exit window and characterized as a particle detector. The negligible intrinsic noise of the device provides an excellent signal-to-noise ratio, even for energetic proton incidence. Besides, the outstanding results of the radiation-hardness test indicate a wider possible range of device applications, including those that involve high currents of charged particles or long exposure to radiation.
m thick membrane which was made of low cost optical quality scCVD diamond material was fabricated. The membrane was mounted to a flange as a vacuum exit window and characterized as a particle detector. The negligible intrinsic noise of the device provides an excellent signal-to-noise ratio, even for energetic proton incidence. Besides, the outstanding results of the radiation-hardness test indicate a wider possible range of device applications, including those that involve high currents of charged particles or long exposure to radiation.